Welding Defects
When welding is done, the parent(base ) metal is hottest at the point of fusion as you move further from this point temperature decrease progressively due to this various kind of zones create
Types of welding zone:
- Fusion Zone: It is that zone that melts and fuses with base metal
- Heat Affected Zone(HAZ): It is that zone in which metal metallurgical properties is affected by the heat but is not melted
- Weld Metal Zone(WMZ): In this zone, it consists of weld metal. It includes metal that melt, resolidifies, filler material (any filler material if use).
- Weld zone : Weld zone = HAZ + HAZ
- Now we know the basic terms of the different zone in welding let's see various defects
DEFECTS IN WELDING :
Cracks :
There are different kind of cracks micro cracks (small crack only able to see under a microscope), macro cracks (bigger than micro can be seen by naked eyes) , fissures crack (wide cracks)
Reasons Of Cracks :
- Structural stresses in metal (heavy shrinkage of metal,high amount of sulphur, rigid clamping etc)
- Cold Cracking : Improper welding conditions, presence of unwanted gas , wrong filler material use in welding, high cooling rate results formation of martensite and other brittle phases
- Corrosion
- Metal defects on which welding going to happen
- Internal Stresses formed due to various operations done on metals before welding
Remedies:
- Proper preheating of metal
- Cleaning of joint properly so that there is not grease ,oil ,moisture is there during welding
- Slow cooling also helps to reduce cracking
- Use correct filler material during welding
- Proper shielding is done to remove unwanted gases
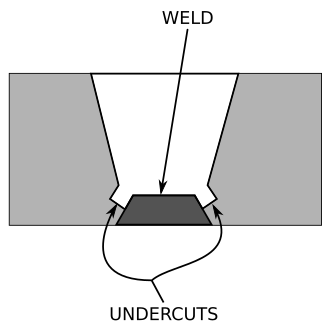
UnderCut :
It is basically a undercut groove melted into the base metal adjacent to the toe of the weld
- Improper Positioning of electrode
- High temperature of the torch tip (temperature higher than required temperature)
- The feeding of filler rod is not uniform
Remedies of undercut :
- Adding additional metal to groove
Porosity or Voids :
During welding porosity /voids are formed they weak the welds and increase the stress on welding which cause a crack in the welds
Cause:
Cause:
- During welding such as oxygen, nitrogen and hydrogen are absorbed by the molten metal. During cooling, if they are not able to escape it will cause porosity and voids
Remedies :
- During welding make sure you properly clean the joints from moisture,dirt , oil and provide proper shielding
Lack of fusion :
Poor adhesion (adhesion means different or separate metals here) of the weld bead to the base metals or weld bead does not start from the root of the weld groove
Cause :
- Low current and voltage which produce less heat input
- the surface is not clean
- Incorrect weld diameter is used for welding
- Welding speed is fast
Remedies
- Use high current and low voltage for better heat input
- Use right electrode diameter
- Clean the surface properly where welding is going to happen
Inclusion:
During welding, if slag, scale or dirt is entrapped in the weld deposit it is called inclusion
Reasons of happening inclusion
Reasons of happening inclusion
- Improper Cleaning
- Low heat input
- cooling is rate of weld is high
- Incorrect angle is used by welding electrode during welding
- high welding speed
Remedies
- Use correct heat input
- Reduce cooling rate as per the metals so that correct welding can be achieve
- Clean the surface properly
- use welding speed as per the material requirements




0 Comments
if you are not getting it then ask i am glad to help